
Test article

Researchers find flaws in algorithm used to identify atypical medication orders

Google launches Document AI suite of parsing and processing tools in preview

MIT CSAIL researchers claim their algorithm helps doctors pick the right antibiotics

Researchers show that computer vision algorithms pretrained on ImageNet exhibit multiple, distressing biases

Alphabet’s Project Amber uses AI to try to diagnose depression from brain waves

RPA startup FortressIQ raises $30 million

VB Live
Hailo partners with Foxconn to build edge device for AI inference

Groove raises $12 million to automate sales enablement

Symend raises $52 million to remediate consumer debt with data science

DJI debuts new enterprise drone and cameras

Dtex raises $17.5 million to detect cyberthreats with AI while preserving privacy

Smart device maker Wink demands customers pay up or lose features
GitHub launches Codespaces for browser-based coding
Health care at ICLR: AI tackles poor data, low resources, and black boxes

Emtrain raises $10 million to prevent workplace harassment with data analytics

BlackCloak: Credentials for 68% of top pharma executives are available on the dark web
Epitopes.world taps AI to predict COVID-19 vaccine success

OpenAI begins publicly tracking AI model efficiency
Google announces Web Vitals, user experience and performance metrics for websites

Open RAN Policy Coalition unites 31 tech companies to lobby U.S. on 5G

GigaSpaces raises $12 million to accelerate AI workloads with in-memory computing
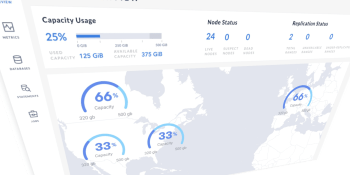
Cockroach Labs raises $86.6 million to store enterprise data in multiple locations

Omilia raises $20 million for AI customer service chatbots

IBM’s Watson AIOps automates IT anomaly detection and remediation

Partner Content
Data storage and AI are driving the evolution of autonomous cars

LinkedIn’s AI generates candidate screening questions from job postings
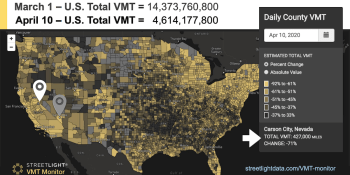
How mobility data could help governments track lockdown compliance

Google releases AI tool for processing Paycheck Protection Program loans

Canalys: Cloud spending hit record $31 billion in Q1 2020, but growth continues to slow

Amazon reports $75.5 billion in Q1 2020 revenue: AWS up 33%, subscriptions up 28%, and ‘other’ up 44%

Microsoft rebrands Visual Studio Online as Visual Studio Codespaces, cuts pricing by over 60%

Vida Health raises $25 million to treat chronic health conditions remotely

CNCF graduates package manager Helm to bring more stability to Kubernetes development

LinkedIn’s AI gives job candidates feedback on their interview answers

Duolingo’s AI drives its English proficiency tests

